CBC Mode
AES具有的五种加密模式中,有一种类似于ECB的加密算法,即为CBC
CBC(Cipher Block Chaining (CBC))将明文分成若干个小段,然后对每一段进行加密处理,对此,我们引入对应的图解
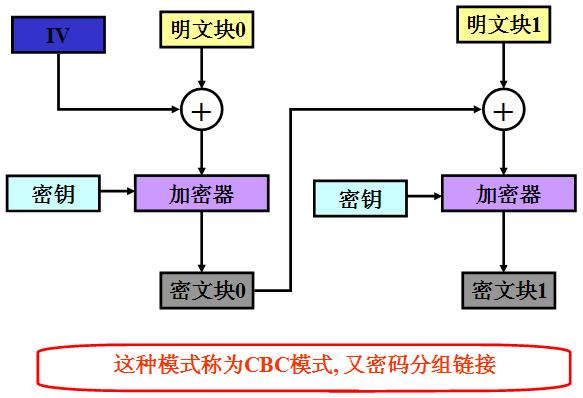
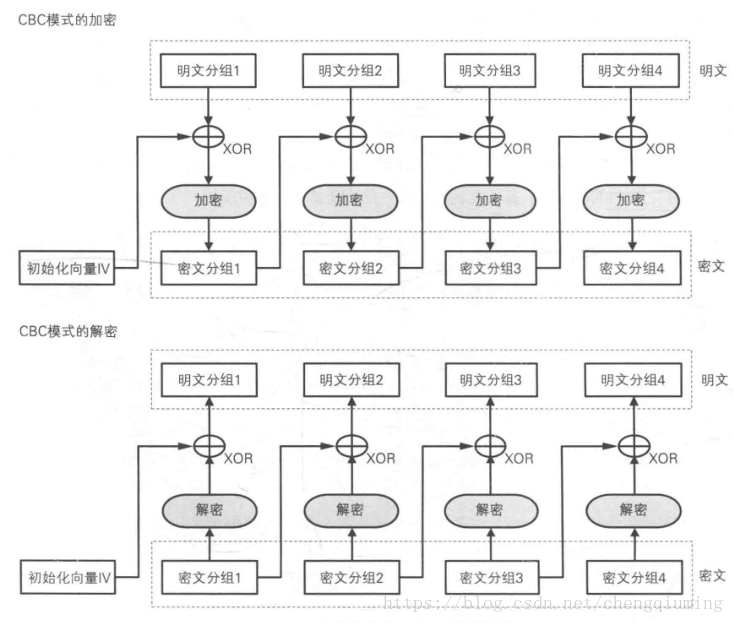
1、初始化向量
初始化向量是一个长度为一个分组的比特序列,其在代码中通常被缩写为IV,密文的长度除以初始化向量的长度,从而得到密文分组的块数,以进行下一步操作
例题:
https://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/
通过访问题设 https://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/encrypt_flag/
可以得到一串密文,通过查看源码中IV的字节个数来对密文进行分块
IV即为一个16字节的初始化向量
我们通过观察随机的密文
1
| {"ciphertext":"655d9981ee826b63ac16998a3c8a98418f5fb1938f5e97fc3cc5472c665916362df4f0ec9d95877313c26c240a1cc3ba"}
|
得到其为96个字符,因为表示形式为十六进制,所以可以判定其字节数为48 bytes
通过IV的字节数对密文分组,分为三组
1
| ciphertext = iv.hex() + encrypted.hex()
|
看到了源码中的这一句,可以推测第一段明文是没用的!!(第一段明文是IV,不需要解出来。。好吧也解不出来)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import requests
from Crypto.Util.number import *
result = requests.get('http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/encrypt_flag')
ciphertext = result.json()["ciphertext"]
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
c1 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[0:16]))[2:]
c2 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[16:32]))[2:]
c3 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[32:48]))[2:]
|
通过访问ciphertext的获取地址,得到ciphertext,然后对ciphertext进行分组,得到每一块的密文
2、密文解密
根据源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| @chal.route('/ecbcbcwtf/decrypt/<ciphertext>/')
def decrypt(ciphertext):
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
cipher = AES.new(KEY, AES.MODE_ECB)
try:
decrypted = cipher.decrypt(ciphertext)
except ValueError as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
return {"plaintext": decrypted.hex()}
|
可以看出来,这个网站给我们提供了解密的步骤,只需要写携带密文访问对应的地址,就可以得到XOR之前的明文,
1
2
3
4
| a1 = requests.get(f'http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/decrypt/{c2}')
a2 = requests.get(f'http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/decrypt/{c3}')
m1 = a1.json()["plaintext"]
m2 = a2.json()["plaintext"]
|

再根据上述算法:
m2为密文分组3解密之后的结果、
m1为密文分组2解密的结果、
c2为密文分组2、
c1为密文分组1、
(全过程中IV是不需要管的)
接下来:m2 XOR c2 得到明文分组3;m1 XOR c1得到明文分组2
组合俩个片段就可以得到FLAG
wp:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| import requests
from Crypto.Util.number import *
result = requests.get('http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/encrypt_flag')
ciphertext = result.json()["ciphertext"]
ciphertext = bytes.fromhex(ciphertext)
c1 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[0:16]))[2:]
c2 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[16:32]))[2:]
c3 = hex(bytes_to_long(ciphertext[32:48]))[2:]
print(c1)
print(c2)
print(c3)
a1 = requests.get(f'http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/decrypt/{c2}')
a2 = requests.get(f'http://aes.cryptohack.org/ecbcbcwtf/decrypt/{c3}')
m1 = a1.json()["plaintext"]
m2 = a2.json()["plaintext"]
M1 = int(m1, 16) ^ int(c1, 16)
M2 = int(m2, 16) ^ int(c2, 16)
print(long_to_bytes(M1) + long_to_bytes(M2))
|



